SSDs
Recent Articles
Sort Options:

Here's the first ever test of the world's largest SSD, and yes, an even bigger 246TB SSD may well land before the end of 2025
Solidigm's D5-P5336 SSD, boasting 122.88TB capacity, prioritizes density and efficiency over speed, retailing at $12,400. While it faces competition, its design is crucial for modern data centers, especially as demand for high-capacity storage surges.
Here's why I'll neever trust an SSD for long-term data storage
The article highlights the advantages of SSDs over mechanical hard drives, emphasizing their speed and reliability. The author shares personal experience with SATA SSDs and the Corsair MP600 PCIe 4.0 SSD, while acknowledging the continued importance of HDDs for secure storage.
5 mistakes to avoid when using SSDs in RAID
The article explores the evolving landscape of storage solutions, highlighting the continued relevance of RAID configurations with SSDs. It emphasizes the benefits of redundancy and speed while cautioning against common pitfalls in SSD RAID setups.

This is what a 1000TB SSD could look like next year: New E2 Petabyte SSD could accelerate transition from hard drives
The emerging E2 SSD form factor aims to bridge the gap in enterprise data storage, targeting warm data with high capacity and efficiency. Supported by industry leaders, E2 SSDs promise significant advancements in storage performance and infrastructure integration.
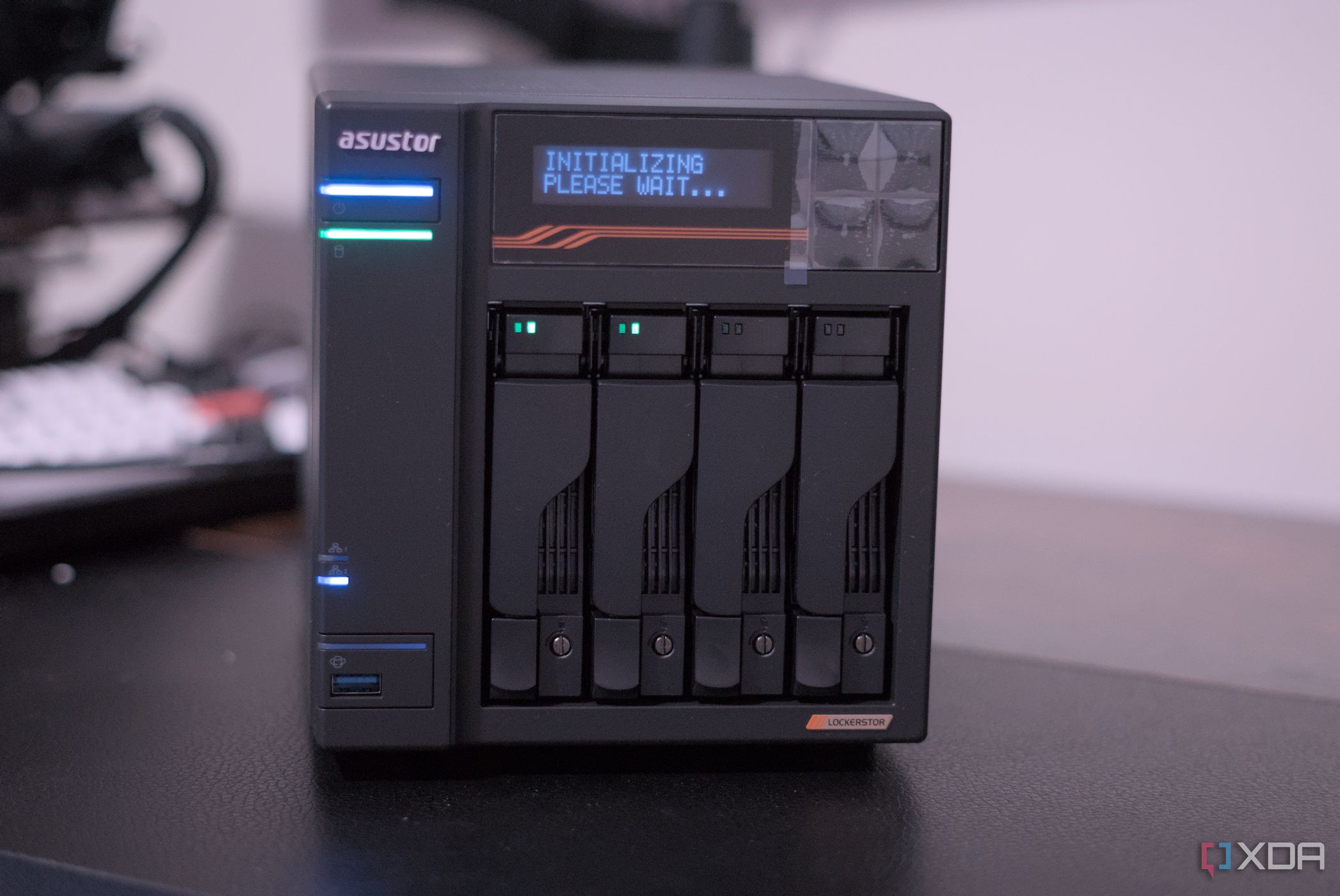

I added SSD caching to my NAS and now I'll tell you why you shouldn't
Solid-state drives (SSDs) offer speed and reliability over traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), but their high cost and limited capacities pose challenges. The authors caution against using NVMe drives for data caching in network-attached storage (NAS) systems.
A new SSD form factor can house a staggering 1,000,000 GB of storage – E2 drives could store 11,000 4K movies with 80W power draw
E2 introduces an innovative flash form factor, promising enhanced performance and efficiency for data storage solutions. This advancement aims to meet the growing demands of modern computing, positioning E2 as a key player in the evolving tech landscape.

Why you shouldn't install NVMe SSD caching inside your Windows PC
The article highlights the transformative impact of solid-state drives (SSDs) on data storage, enhancing modern devices and improving older hardware performance. It discusses technologies like Intel Optane and AMD StoreMI, emphasizing their relevance for servers and NAS systems.
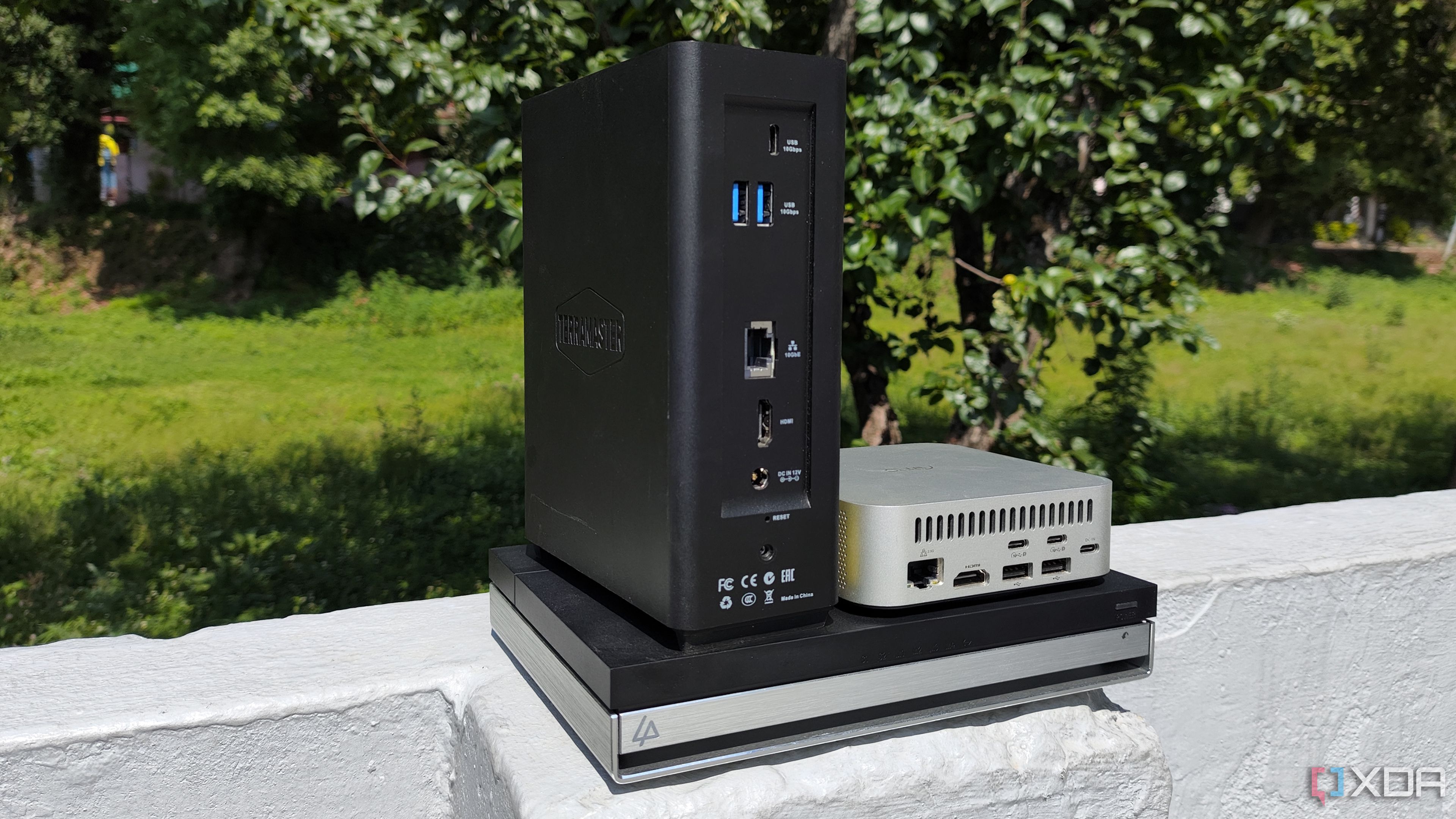

All-SSD NAS devices are the best companion for frequent travelers
The rise of all-SSD Network-Attached Storage (NAS) models is transforming home labs, moving away from traditional bulky HDD setups. This shift promises quieter, more efficient data management for self-hosting and data-hoarding workstations.

World's largest SSD is on sale for almost $12,400 and yes, it is quite a bargain - if you can afford it of course
Solidigm's 122.88TB D5-P5336 SSD is now available for $12,399, designed for hyperscale data infrastructures. Featuring 192-layer QLC NAND, it promises high endurance and performance, making it ideal for enterprise storage handling AI and data-intensive workloads.

Sandisk could use new architecture called Stargate to power its 256TB and 512TB SSDs in 2026 and beyond
SanDisk, now independent from Western Digital, is set to launch its new Stargate SSD controller, enabling high-capacity enterprise drives. With ambitious plans for 256TB and 512TB models by 2026 and 2027, the company aims to revolutionize storage solutions.

5 reasons I’m buying SSDs, not HDDs
The article discusses the importance of managing digital data effectively, highlighting the need for fast local storage solutions for tasks like video editing, while acknowledging that not all data requires long-term preservation.